Introduction
This section explains how the output-module deals with CustomFields in Shopware. It will also explain how you have to prepare your documents in order to map custom fields to Shopware.
The output-module is able to create and fill CustomFields and CustomFieldSets. There is currently the restriction that
only CustomFields of the type "text" can be created. However, the filling of CustomFields of other types is possible.
Basics
The trait AttributeAware provides an AttributeGroupCollection. The elements within this collection are used to map custom field
sets and custom fields to Shopware:
- The document
AttributeGroupis mapped to aCustomFieldSet-The documentAttribute(which is "owned" by anAttributeGroup) is mapped to aCustomField. The owningAttributeGroupdetermines to whichCustomFieldSettheCustomFieldbelongs. - The module will create
CustomFieldSets,CustomFieldSetRelationsandCustomFieldsautomatically if they are not existing yet. However, this behaviour is configurable. -
CustomFieldSetsandCustomFieldsare created "on the fly" as soon as a field/set is found that does not yet exist in Shopware. - CustomFields are filled together with the entity in the upsert request.
- Attributes / CustomFields will always be included in upsert requests. Timestamps of the attributes are ignored.
- Attributes are always converted to custom field values, even if the custom field is not existing in Shopware.
Custom Field Sets
Target: custom_field_set and custom_field_set_relation
Source: Elio\CommonBundle\Document\Attribute\AttributeGroup
| Target Field | Source Path | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| name | name |
Technical name of the set which is unique in Shopware |
Custom field sets are generated from AttributeGroups:
- The name of the AttributeGroup (
AttributeGroup::name) corresponds to the technical name of the custom field set (CustomFieldSet::name) in Shopware. - All
Attributesthat are part of theAttributeGroupare converted to a custom field of this set.
Custom Field Set Relations
- Depending on the type of document in which the
AttributeGroupis embedded, a suitableCustomFieldSetRelationis generated in
Shopware. - If the same
AttributeGroupis added to different documents, the module will generate two relations in Shopware. - It is not possible to remove relations. If you remove an
AttributeGroupfrom all documents the relation to the product-entity will stay in the shop.
How to Create a Custom Field Set
This example shows you how to create a custom field set in Shopware by the help of an AttributeGroup.
An AttributeGroup "synqup_data_set" is assigned to a Product and a Customer:
$product = ...;
$customer = ...
$attributeGroup = new AttributeGroup('synqup_data_set');
$product->setAttributeGroups(new AttributeGroupCollection([$attributeGroup]));
$customer->setAttributeGroups(new AttributeGroupCollection([$attributeGroup]));
// persist and flush ...
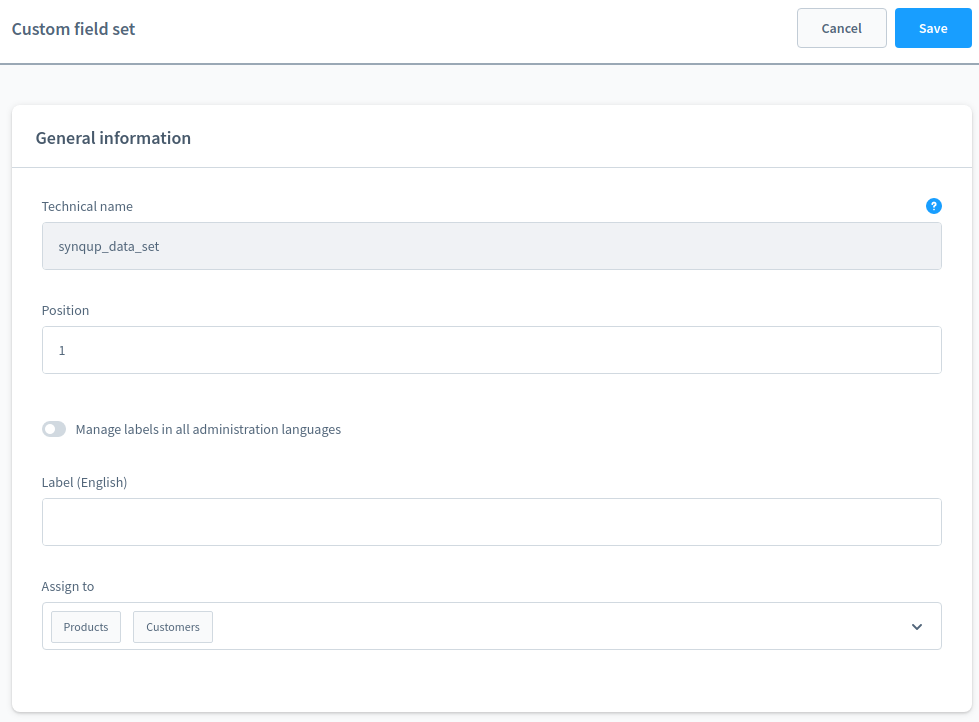
The module will create a CustomFieldSet with the technical name "synqup_data_set". The CustomFieldSet is assigned to the Shopware
entities Product and Customer:
Custom Fields
Target: custom_field
Source: Elio\CommonBundle\Document\Attribute\Attribute
| Target Field | Source Path |
|---|---|
* name |
name - technical name of the custom field field which is unique in Shopware |
| type | Always 'text'. Other field-types cannot be created yet |
| config | Generated automatically by the module |
| customFieldSetId | Determined from the AttributeGroup::name to which the Attribute belongs |
- An
Attribute, owned by anAttributeGroup, is converted to aCustomField. - The custom field is assigned to the custom field set that corresponds to the owning
AttributeGroup.
How to Create and Fill Custom Fields
This example shows you how to create a custom field and how to fill it with data. The example will use the following code:
$attributeGroup = new AttributeGroup(name: 'synqup_data_set'); # converted to a CustomFieldSet with technical name "synqup_data_set"
$attributeGroup->addAttribute( # converted to a CustomField with technical name "translated_data_field"
new Attribute(
name : 'translated_data_field',
valueLabel: TranslationCollection::create([Locale::en_GB, 'en-GB'], [Locale::de_DE, 'de-DE']) # the value used in translated entities
)
);
$attributeGroup->addAttribute(
new Attribute(
name : 'non_translated_data_field',
value: 'non-translated value' # the value used in non translated entities
)
);
$product = ...;
$customer = ...;
$product->setAttributeGroups(new AttributeGroupCollection([$attributeGroup]));
$customer->setAttributeGroups(new AttributeGroupCollection([$attributeGroup]));
Create Custom Fields
First, lets take a look on how to create a custom field. The following has to be considered:
- The document
Attributeis mapped to aCustomField - The 'parent'
AttributeGroupof theAttributedetermines theCustomFieldSettheCustomFieldwill be a part of - The name of the
Attribute(Attribute::name) determines the technical name of theCustomFieldin Shopware
Following these rules the code from above leads to the following result in the administration panel:
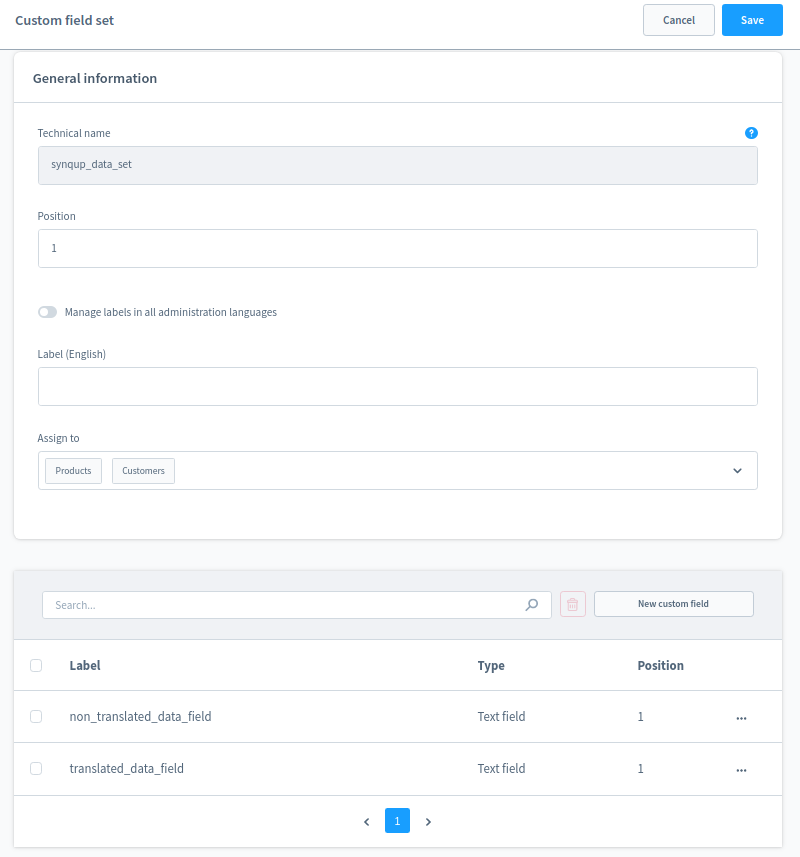
- The module creates two custom fields: "translated_data_field" and "non_translated_data_field".
- The custom fields are assigned to the custom field set that belongs to the owning
AttributeGroup- in this case "synqup data set"
Fill Custom Fields - Translated and Non-Translated Custom Fields
Regarding the values that are transferred to Shopware you have to distinguish between custom fields that are mapped to translated Shopware entities (e.g. Products) and non-translated entities (e.g. Customers or Orders).
Translated Entities
The following principle applies to entities with translated custom fields (e.g. products):
- The module tries to read a translated value from the
TranslationCollectionatAttribute::valueLabel. This is done for every mapped language. - The field
Attribute::valueis used as fallback for the default system language - but only if the fieldAttribute::valueLabelis not available.
Following these rules, this example will lead to the following result in the database (field custom_fields of
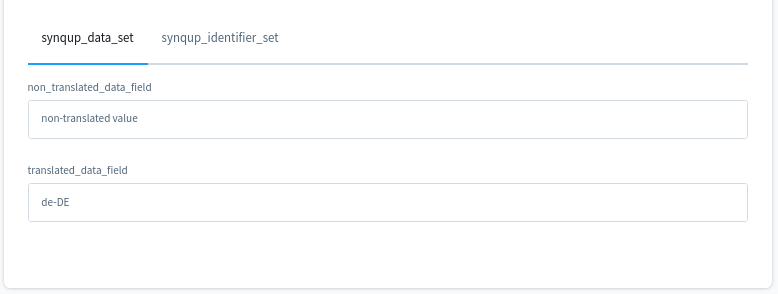
the product_translation table). This is the result for the system language (de-DE):
{
"translated_data_field": "de-DE",
"non_translated_data_field": "non-translated value"
}
This is the result for the optional language (en-GB):
{
"translated_data_field": "en-GB",
"non_translated_data_field": null
}
- As you can see, the translated values were read from
Attribute::valueLabel, wherever possible - Since the "non_translated_data_field" does not provide the field
Attribute::valueLabel, but the fieldAttribute::value, the value was read fromAttribute::value
For the sake of completeness, this is the result (for the system language de-DE) on the product detail page of the administration panel:
Non-Translated Entities
The following principle applies to entities with non-translated custom fields (e.g. customer or order):
- The value for the custom field is read from the field
Attribute::valueby default. - If the field
Attribute::valueis null, the module tries to read a fallback value from the fieldAttribute::valueLabelfor the system locale. - If both values are set the field
Attribute::valuehas higher priority.
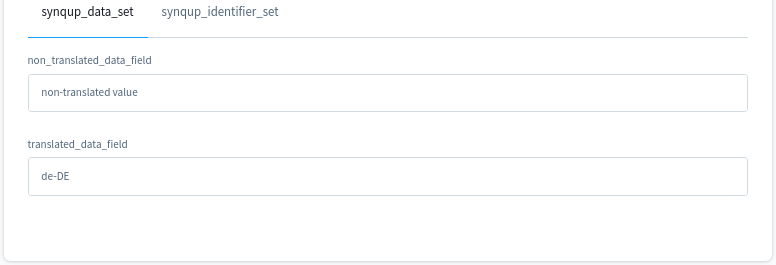
Following these rules, this example will lead to the following result in the database (field custom_fields of the customer table):
{
"translated_data_field": "de-DE",
"non_translated_data_field": "non-translated value"
}
For the sake of completeness, this is the result on the customer detail page of the administration panel:
Configuration
You can manage how the module handles custom fields via configuration:
{
"customFields":{
"enabled": true,
"autoCreate": true,
"ignore": {...},
"create": {...},
"fill": {...}
}
}
-
enabled: Controls whether custom fields and -sets are created/filled at all. -
autoCreate: Controls whether custom fields and -sets are created automatically. -
ignore: Section to configure which custom fields and -sets are ignored entirely by the module (see "Custom Field Filter") -
create: Section to configure which custom fields and -sets may be created by the module (see "Custom Field Filter") -
fill: Section to configure which custom fields and -sets may be filled with values (see "Custom Field Filter")
Custom Field Filter
It is possible to exclude certain custom fields and/or -sets from getting created or filled with data via configuration.
There are three options for your filter available: create, fill and ignore (see below for details).
{
"customFields": {
"...": "...",
"create|fill|ignore": {
"whitelistMode": true|false,
"sets": [
"synqup_data_set",
"..."
],
"fields": [
"translated_data_field",
"non_translated_data_field",
"..."
]
}
}
}
-
whitelistMode: Configures the filter to act like a whitelist (set totrue) or ignore-list (set tofalse)-
true: The filter behaves like a whitelist. Used to specifically include certain sets and fields. This allows the module to handle only a specific selection of sets and fields. -
false: The filter behaves like an ignore-list. Used to specifically exclude certain sets and fields. You forbid the module to handle a specific collection of fields and sets.
-
-
sets: Contains a list of technical names of custom field sets (CustomFieldSetEntity::name/AttributeGroup::name) that will be included/excluded during custom field handling. -
fields: Contains a list of technical names of custom fields (CustomFieldEntity::name/Attribute::name) that will be included/excluded during custom field handling.
Note that the identifier custom field is not affected by this configuration.
Create Filter
The create section is used to configure which custom fields and `custom field sets are automatically created.
Whitelist Mode
-
setscontains allCustomFieldSetsthat are created. ACustomFieldcontained in aCustomFieldSetwill only be created if it is whitelisted infields. -
fieldscontains all fields that are created. The name of the "parent"CustomFieldSetmust be available insets, otherwise the field is ignored.
Ignore Mode
-
setscontains allCustomFieldSetsthat are not allowed to be created. AllCustomFieldsthat are part of one of theseCustomFieldSetsare ignored. -
fieldscontains allCustomFieldsthat are not created automatically. Theparentset does not have to be included insets, so you can exclude specific CustomFields from getting created.
Fill Filter
The fill section is used to configure which CustomFieldSets and CustomFields are automatically filled with data.
Whitelist Mode
-
setscontains allCustomFieldSetswhose "children" (=CustomFields) are filled with data. AllCustomFieldsthat are part of theCustomFieldSetwill be whitelisted and filled automatically. In other words: If a set is allowed, every field of the set will be allowed (=filled with data) as well. -
fieldscontains allCustomFieldsthat are filled with data. If the "parent" set is not available insetsthisCustomFieldwill be filled anyway which makes it possible to allow individualCustomFieldsto be filled.
Ignore Mode
-
setscontains allCustomFieldSetswhose fields are not filled. AllCustomFieldsthat are part of an ignoredCustomFieldSetare automatically ignored as well. -
fieldscontains allCustomFieldsthat are not filled with data. Theparentset does not need to be included insetswhich makes it possible to ignore individual fields
Ignore Filter
The ignore section is used to configure which CustomFieldSets and CustomFields are ignored entirely. This is a combination of
the create and fill sections.
Warning: If the ignore section contains at least one element both the create and fill sections are ignored entirely. This
section is applied to both the create- and fill-sections.
Different Custom Field Types
As already mentioned it is only possible to create custom fields of type text. However, it is possible to fill custom fields of any type. The following types of custom fields are available in Shopware (07-2022):
- Text field
- Text editor
- Number field (integer or float)
- Number field
- Date/time field
- Checkbox
- Active switch
- Select field with single or multi selection
- Colour picker
- Entity select with single or multi selection
- Media field
- Price field
You can find more information in the documentation of Shopware.
The purpose of this section is to give you a first orientation/example on how to fill custom fields of different types. This is by no means a complete documentation on custom fields in Shopware that covers every edge-case that might come up during filling custom fields of different types.
Attributes
The following example contains Attributes for every aforementioned custom field type.
$customer = $this->documentManager->find(Customer::class, "604f0a46ca2c165eae7380ee");
$typedCustomFieldSet = new AttributeGroup('typed_custom_field_set');
# text field and text editor
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_text_field', 'text-value'));
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_text_editor', '<b>bold-text </b> - <i>italic-text </i>'));
# number field (integer and float)
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_number_integer', 51));
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_number_float', 5.1));
# datetime
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_date_time', new DateTime()));
# checkbox and active switch
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_checkbox', true));
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_active_switch', false));
#
# select fields
#
# use technical names of the select options
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_select_field', 'select_option_1'));
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_select_field_multi', ['select_option_1', 'select_option_2']));
# color picker
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_colour_picker', '#000000'));
#
# entity selection fields
#
# requires entity uuids
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_entity_select', 'c3a2ca36f912a498f7ba57a50211cbee'));
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(
new Attribute('type_entity_select_multi', ["c3a2ca36f912a498f7ba57a50211cbee", "780d02994e88edd73ba43ec5273df8c9"])
);
#
# media fields
#
# requires uuid of a media object
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_media', 'd11e8d2dfb9a481081fbfd41778cd35b'));
# price
$price = [
[ "currencyId" => "b7d2554b0ce847cd82f3ac9bd1c0dfca",
"net" => 15.0,
"gross" => 15.0,
"linked" => true,
"listPrice" => null,
"percentage" => null,
"regulationPrice" => null
]
];
$typedCustomFieldSet->addAttribute(new Attribute('type_price_field', $price));
$customer->setAttributeGroups(new AttributeGroupCollection([$typedCustomFieldSet]));
API Request
This is the Sync API request that the module would generate from the example above.
[
{
"action": "upsert",
"entity": "customer",
"payload": [
{
"id": "cba00a6cc2b1360c7bb2d4891aca99ce",
"customFields": {
"type_text_field": "text-value",
"type_text_editor": "<b>bold-text </b> - <i>italic-text </i>",
"type_number_float": 5.1,
"type_number_integer": 51,
"type_date_time": "2030-07-29T12:15:00+00:00",
"type_checkbox": true,
"type_active_switch": true,
"type_select_field": "select_option_1",
"type_select_field_multi": [
"select_option_1",
"select_option_2"
],
"type_colour_picker": "#000000",
"type_entity_select": "c3a2ca36f912a498f7ba57a50211cbee",
"type_entity_select_multi": [
"c3a2ca36f912a498f7ba57a50211cbee",
"780d02994e88edd73ba43ec5273df8c9"
],
"type_media": "d11e8d2dfb9a481081fbfd41778cd35b",
"type_price_field": [
{
"currencyId": "b7d2554b0ce847cd82f3ac9bd1c0dfca",
"net": 15.0,
"gross": 15.0,
"linked": true,
"listPrice": null,
"percentage": null,
"regulationPrice": null
},
{
"currencyId": "89df0abdbab54dc4858d30777a9226bf",
"net": 18.0,
"gross": 18.0,
"linked": true,
"listPrice": null,
"percentage": null,
"regulationPrice": null
}
]
}
}
]
}
]

