Choosing the right middleware is crucial for success in e-commerce. In this article, you will learn how the optimal solution can support your company on the path to greater efficiency and growth! Which criteria you should pay attention to.
Digitalization means one thing above all: data, data and more data. New applications and systems are constantly coming onto the market, especially in e-commerce, which make it possible to optimize business processes and offer customers a smooth shopping experience. And middleware is increasingly being used to make this experience even better.
What is middleware?
Middleware refers to software solutions that act as an intermediary between different systems. Such applications close gaps between applications, tools or databases. This not only enables a smooth flow of data, but also the communication and integration of different applications and systems.
The middleware is also illustrated very well and simply in this video:
Middleware has been part of software technology since the late 1960s and can be seen as a category for a large number of modern software components.
Middlewares can span a variety of functions, including the integration of enterprise applications, application runtimes and different cloud services. Tasks such as data management, provision of application services, messaging, authentication and the management of APIs are also firmly anchored in their repertoire.
What are the benefits of e-commerce middleware?
But how can this “intermediate application” support e-commerce? Middleware helps, for example, to connect content management systems, merchandise management systems, payment providers and logistics service providers and to seamlessly exchange information between them. This enables companies to implement more efficient business processes and ultimately offer a better customer experience.
In summary, this results in these four advantages:
Simplified integration and communication:
With middleware as a central interface, companies can manage their system landscape more efficiently and simplify communication between the various applications and systems.
Improved data consistency and quality:
Intermediary software of this kind ensures that data is exchanged consistently and in high quality between the various systems. Data silos can thus be significantly reduced. This not only improves decision-making, but also helps to minimize errors.
Greater scalability and flexibility:
Middleware enables the seamless integration of new applications and systems without having to completely overhaul the existing architecture. This promotes the scalability of the company and gives it the flexibility to react quickly to market changes or new technologies.
Reduced costs and complexity:
By using middleware, companies can reduce the complexity of their IT infrastructure and minimize the costs of developing and maintaining individual interfaces.
More time and resources:
The introduction of such a tool automates and digitalizes previously manual workflows and processes. This leaves more time and resources for other projects and topics.
Middleware examples: Message-oriented middleware, platform middleware and co.
As already mentioned above, there are different types of middleware.
These are the most important species:
- Message-oriented middleware (MOM) allows communication and message exchange between application components that use different message protocols. In addition to converting messages between applications, MOM also handles routing to ensure that the messages always reach the relevant components in the correct order. Examples of this are message queues and message brokers.
- Data or database middleware simplifies access to backend databases and makes it easier to interact with them. In general, database middleware is a variant of SQL database servers.
- Platform middleware, also known as application platform middleware, provides comprehensive support for application development and accelerates the deployment of applications. It does this by providing a runtime hosting environment, such as a Java runtime environment (Java RE) or containers, or both, for the application or business logic. Platform middleware can include or combine different types of middleware, including enterprise application servers, web servers and content management systems.
- Enterprise application integration middleware enables companies to create an integration hub. This is a standardized way to connect all applications, application components, business processes and backend data sources in the extended enterprise environment. About a decade ago, the most common type of middleware used for enterprise application integration was the enterprise service bus (ESB), which acted as the central integration hub within a service-oriented architecture (SOA). Today, Integration-Platform-as-a-Service (iPaaS) enables companies to seamlessly connect applications, data, processes and services across on-premises, private and public cloud environments – without the need to purchase, install, manage and maintain the integration middleware (and underlying hardware) in their own data center.
Future viability secured through middleware in e-commerce
In order to remain competitive, companies in a fast-moving industry such as e-commerce must be able to continuously adapt and expand their system landscape.
Middleware solutions help companies to remain fit for the future by
- Providing a central platform for innovation: With middleware as a central data hub, companies can quickly and efficiently integrate new technologies and innovations into their existing system landscape without disrupting existing processes. This makes it possible to continuously utilize emerging trends and technologies and thus secure a competitive advantage.
- Enabling a consistent customer experience: Such solutions ensure that all systems and applications in e-commerce communicate with each other and exchange information seamlessly. This allows companies to ensure a consistent and seamless customer experience, regardless of the technologies or platforms used.
- Promoting data analysis and business intelligence: By collecting and processing data centrally, an intermediate application enables companies to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends and business processes. This information can be used to make data-driven decisions and adapt the business strategy accordingly.
- Support multi-channel and omni-channel strategies: Middleware solutions enable companies to expand their presence across multiple sales channels, increasing their reach and visibility. The central data hub ensures that all channels are linked and provide consistent information to enable a uniform customer experience across all channels.
Practical examples of successful middleware implementations in e-commerce
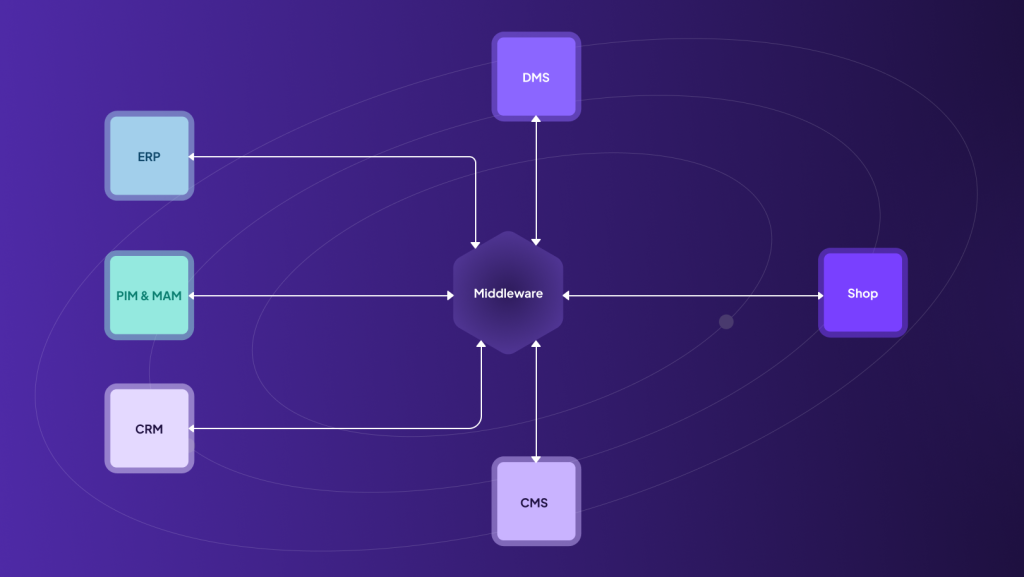
What can this look like in practice? In e-commerce, the use of middleware makes sense in four areas in particular. For example, such a solution can connect the enterprise resource planning system (ERP) with the online store. This allows you to easily manage your product data, stock levels, orders and invoices centrally and effectively.
Integration between your Product Information Management (PIM) system and Media Asset Management (MAM) system and your online store also makes sense. The connection enables smooth data exchange and automated synchronization of your product data, media resources, categories and attributes. This seamless integration not only improves the consistency and up-to-dateness of your product information, but also enables you to create an impressive shopping experience for your customers.
When talking about PIM and MAM, the digital asset management (DAM) tool must not be forgotten. Manage your digital assets more efficiently by integrating your DAM system with your online store and creating a central platform for managing and providing images, videos and other media files.
You can also increase your customer service and sales by linking your CRM system with your online store and enabling personalized customer communication. This allows you to use comprehensive customer information, purchase histories and preferences to provide personalized offers and recommendations.
One middleware provider of a solution that can implement all of this is “synQup”. The solution serves as a central data hub that integrates all systems from the system landscape (ERP, PIM, DAM and CRM) and allows them to communicate with each other. By enabling a seamless exchange of information between the various applications and systems, synQup helps companies to realize more efficient business processes, increase the scalability and flexibility of their IT infrastructure and ultimately offer a better customer experience.
Selection and implementation of middleware in e-commerce
But how do you find the perfect middleware solution? The answer is obvious: there is no one solution. Depending on the criteria, there are a wide variety of options. You should therefore think about functions and other criteria in advance.
The following ten aspects will help you make your choice:
- Integration with existing systems: The middleware should integrate seamlessly with the company’s existing systems and technologies to ensure smooth data exchange and workflows.
- Scalability: In order to keep pace with the growth of the e-commerce business, the solution should definitely be scalable. This also includes the ability to efficiently process both the amount of data and the number of users.
- Flexibility: The middleware should be flexible enough to support different requirements and business processes. This enables adaptation to changing market conditions and business models.
- Security: As sensitive customer data is processed in e-commerce, a robust security infrastructure is essential. The middleware should meet security standards and comply with data protection guidelines.
- Ease of use: A user-friendly interface and clear documentation are crucial to facilitate the implementation and management of the software. This helps to minimize training time for the team.
- Costs: The total cost of ownership, including license fees, implementation costs and ongoing maintenance, should be within the company’s budget. A transparent cost structure is important to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Support and training: Reliable support from the provider is essential. At the same time, training opportunities should be provided to ensure that the internal team can use the solution effectively.
- Performance and speed: Transactions should be processed quickly and reliably. This is particularly important to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Compliance: The middleware solution should comply with industry-specific regulations and compliance requirements, particularly with regard to data protection and payment processing in e-commerce.
- Future-proof: The tool should also keep pace with future developments and technologies in e-commerce to ensure investment security.
Conclusion and outlook for middleware in e-commerce
Middleware in e-commerce offers numerous advantages, which will no doubt have become clear to you while reading this article: From simplifying integration and communication between different systems and applications to improving data consistency and quality. By using a solution such as synQup, companies can future-proof their system landscape and prepare for continuous adaptation to new technologies and market changes. Overall, the use of middleware enables companies to remain competitive and successful in an increasingly complex digital world.